
Internal Resistance and Its Impact on Ni-Cd Battery Performance
Keywords: NiCd battery performance, internal resistance effects, high discharge battery, industrial energy storage Introduction Internal

Keywords: NiCd battery performance, internal resistance effects, high discharge battery, industrial energy storage Introduction Internal

Keywords: NiCd battery internal resistance measurement, battery testing methods, electrochemical impedance, industrial battery diagnostics Introduction
Keywords: NiCd battery resistance factors, nickel-cadmium battery behavior, internal impedance changes, battery maintenance Introduction Although

Keywords: Ni-Cd battery internal resistance, nickel-cadmium battery performance, industrial battery testing, NiCd impedance Introduction Internal

Keywords: OPzV battery life extension, maintenance after repair, battery performance optimization Introduction After successful sulfation
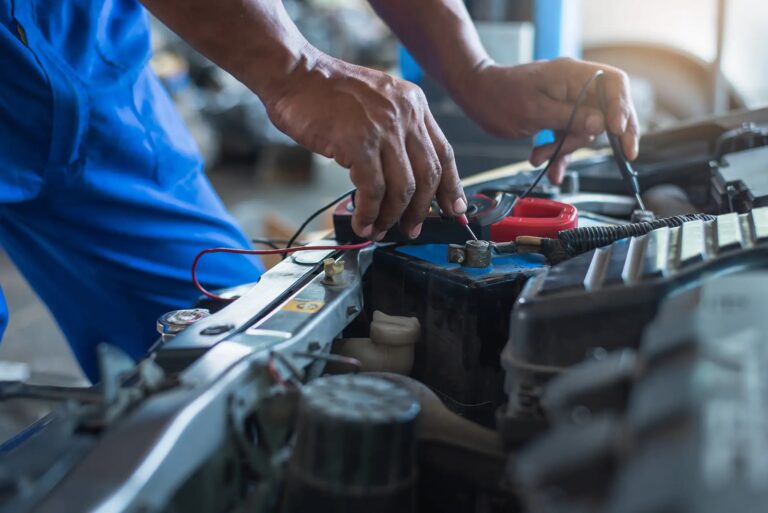

Keywords: OPzV battery repair mistakes, sulfation recovery, gel battery maintenance Introduction While repairing sulfated OPzV
Keywords: OPzV battery desulfator, battery repair device, gel battery restoration, desulfation process Introduction Modern battery

Keywords: OPzV battery repair, sulfation removal, desulfation, gel battery rejuvenation Introduction When sulfation has already

Keywords: OPzV gel battery, sulfation causes, battery maintenance, deep cycle battery care Even the most
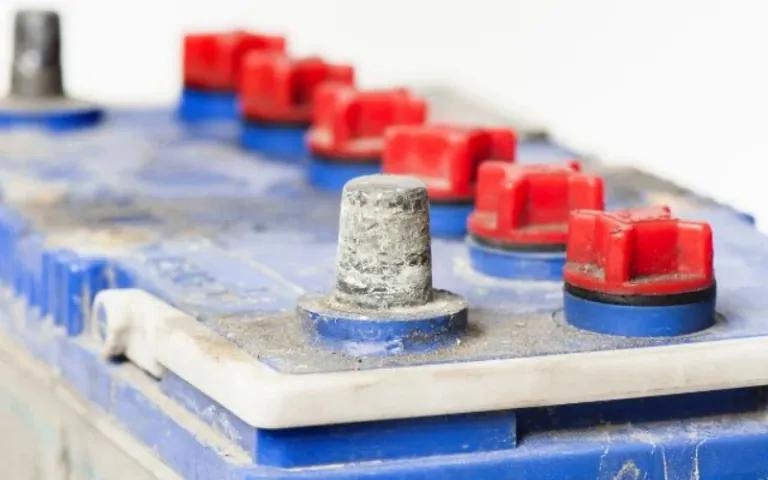

Keywords: OPzV battery sulfation, lead-acid gel battery, battery repair, performance degradation Introduction Sulfation is one