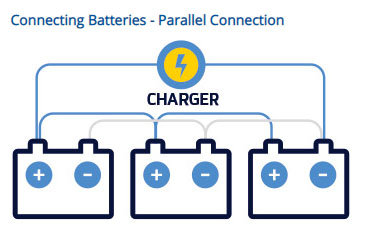
Introduction
Parallel connection expands energy capacity, making it a popular choice for residential and small commercial energy storage systems. While the principle is simple, the electrical behavior of lead-acid batteries creates unique challenges.
Keywords: parallel lead-acid battery connection, battery capacity expansion, off-grid solar battery parallel, current sharing.
1. Unequal Current Sharing
Batteries rarely have perfectly equal internal resistance. As a result:
- The battery with lower resistance provides more current during discharge.
- It receives more charging current during charging.
- It ages faster, reducing the lifespan of the entire bank.
2. Risk of Circulating Currents
Parallel batteries can self-discharge into each other when:
- Their voltages are mismatched
- Their internal resistance differs
This results in unnecessary heat and energy loss.
3. Cable Resistance and Layout Problems
Unequal cable lengths cause resistance differences.
Best practice:
- Use busbars instead of point-to-point wiring.
- Maintain equal cable lengths from each battery to the busbar.
- Ensure sufficient cable thickness.
4. Impact on System Efficiency
Parallel configurations increase total capacity but require stronger cables and careful design to avoid:
- Overheating
- Imbalanced charging
- Shortened battery life
Conclusion
Parallel connection is effective but must be implemented correctly to ensure safety, balance, and long-term durability.