Lithium-ion batteries are popular for their high energy density, efficiency, and long life cycles. However, one of the most important factors that influence their performance is the Depth of Discharge (DoD). This article delves into how DoD affects lithium battery performance and why managing DoD is critical for efficient battery usage.
DoD and Battery Capacity
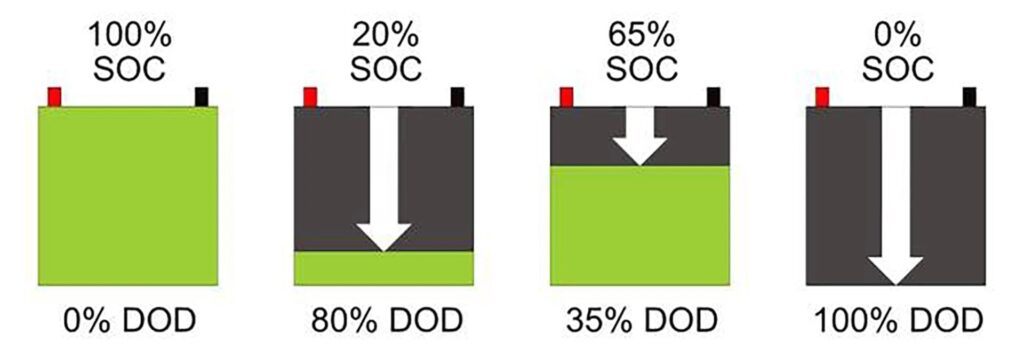
As a lithium battery discharges, its capacity reduces. High DoD usage means a large portion of the battery’s capacity is being used, which can lead to faster wear. Conversely, maintaining a low DoD, such as keeping the discharge below 50%, can significantly extend the usable life of the battery. Batteries are typically rated for a certain number of charge cycles, which depend heavily on the average DoD. A battery cycled at 100% DoD will go through fewer cycles than one at 20%.
Thermal Impacts of High DoD
High DoD discharges also lead to increased heat generation inside the battery. As the internal temperature rises due to a high discharge rate, it can degrade the battery’s components, such as the electrolyte and electrodes. Managing heat effectively by maintaining moderate DoD levels can thus not only improve battery safety but also prolong its life.
DoD in Electric Vehicles and Renewable Energy Systems
In applications like electric vehicles (EVs) or renewable energy storage, DoD is crucial to balance performance and longevity. For EVs, manufacturers may limit the usable capacity (i.e., manage DoD) to prevent deep discharges, ensuring longer battery life. Similarly, in solar storage systems, managing DoD helps optimize the system for both energy efficiency and longevity.