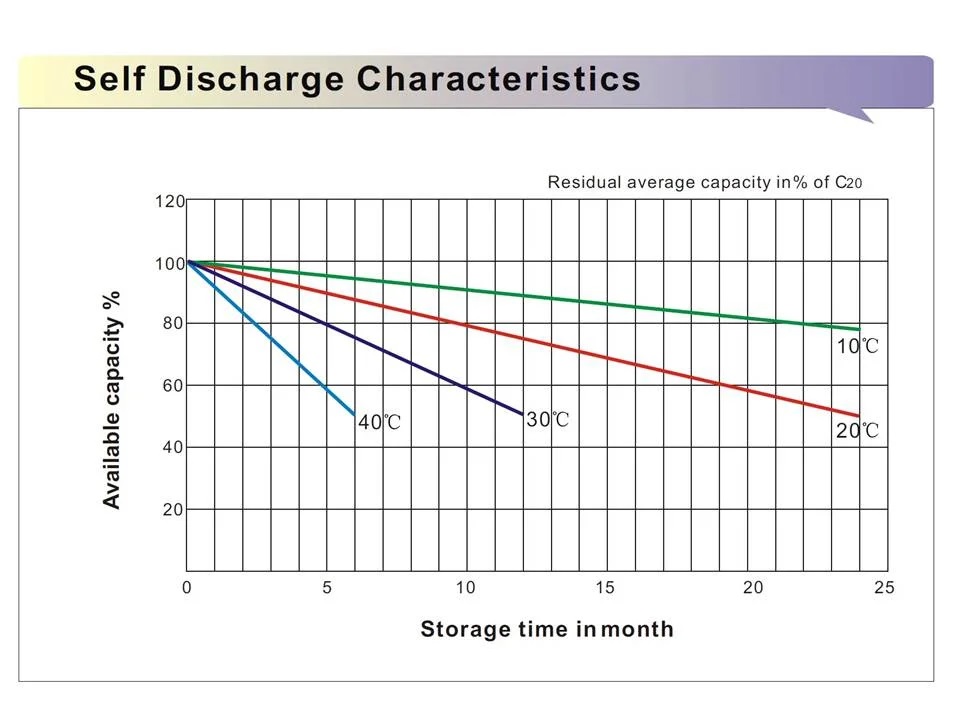
Lead-acid batteries can experience self-discharge over time, where they lose charge even when not in use. Here are some ways to treat and minimize self-discharge in lead-acid batteries.
- Regular Charging: Keep the battery fully charged whenever possible. Regular charging helps counteract self-discharge by replenishing lost charge and maintaining the battery’s state of charge.
- Temperature Control: Store the battery in a cool, dry place. High temperatures can accelerate self-discharge, so keeping the battery in a cooler environment can help reduce this phenomenon.
- Disconnecting Loads: If the battery is connected to devices or equipment when not in use, disconnect them to prevent parasitic loads that can contribute to self-discharge.
- Battery Maintenance: Check the battery regularly for any signs of corrosion, damage, or electrolyte levels. Proper maintenance ensures the battery operates efficiently and reduces the likelihood of self-discharge due to issues such as sulfation or internal resistance.
- Float Charging: If the battery will be in storage for an extended period, consider using a float charger or trickle charger. These chargers supply a low-level charge to the battery, which helps offset self-discharge without overcharging.
- Equalization Charging: Periodically perform equalization charging if recommended by the battery manufacturer. This process helps balance the charge among the battery cells and can reduce the effects of self-discharge.
- Using Battery Desulfators: Battery desulfators can help break down sulfate crystals that can form on the battery plates over time, which can contribute to self-discharge and reduced battery capacity.
- Battery Additives: Some additives are available that claim to reduce self-discharge and extend battery life. These additives are typically mixed with the electrolyte according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
By following these practices, you can minimize self-discharge and ensure that lead-acid batteries maintain their charge and performance over time.