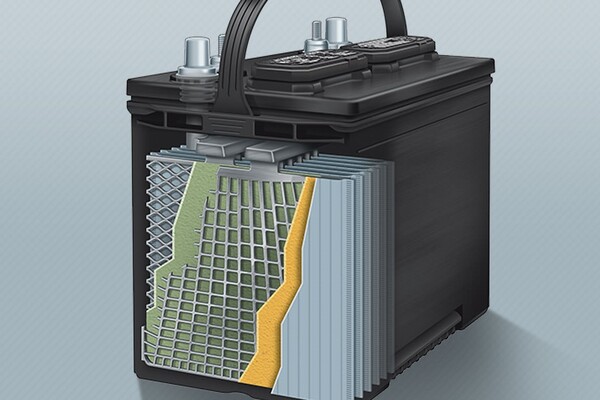
The terms “flooded battery” and “lean battery” typically refer to different types of lead-acid batteries, which are commonly used in various applications, including automotive, marine, and backup power systems.
Flooded Battery
- Design and Structure:
- Electrolyte: Contains a liquid electrolyte composed of sulfuric acid and water that freely moves around the battery cells.
- Maintenance: Requires regular maintenance, including checking and topping off the electrolyte levels with distilled water.
- Performance:
- Discharge/Charge: Can handle deep discharges and charges but has a moderate cycle life compared to other battery types.
- Cost: Generally less expensive due to simpler manufacturing processes.
- Usage:
- Commonly used in automotive applications, solar energy systems, and backup power supplies where regular maintenance can be performed.
- Advantages:
- Lower initial cost.
- Can handle overcharging better than some sealed batteries due to venting of gases.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires regular maintenance.
- Can spill and release gases, necessitating proper ventilation and safety measures.
- Heavier and bulkier compared to other types.