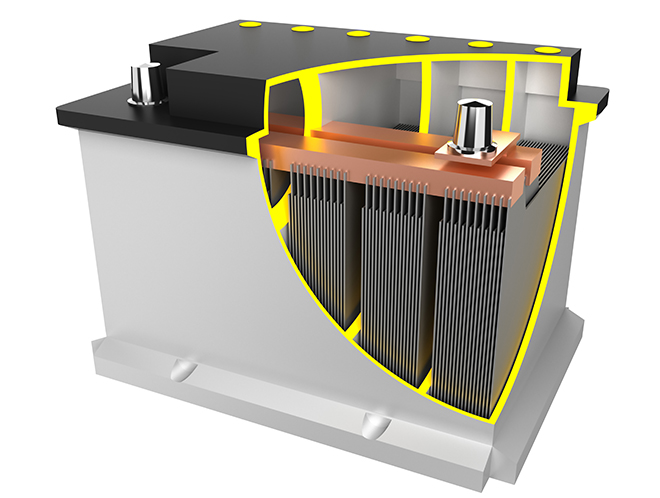
The plates in lead-acid batteries play a crucial role in the electrochemical reactions that produce electrical energy. Lead-acid batteries have positive and negative plates that are immersed in an electrolyte solution, typically sulfuric acid. The two types of plates are typically made of lead-based materials, and their structure and composition contribute to the battery’s overall performance.
- Positive Plates:
- Material: The positive plates are typically made of lead dioxide (PbO2).
- Role: During the discharge (when the battery is providing electrical power), the positive plates undergo a chemical reaction where lead dioxide (PbO2) is reduced to lead sulfate (PbSO4). This process releases electrons into the external circuit, creating the flow of electric current.
- Charge Reaction: PbO2 + H2SO4 + 2H+ + 2e- → PbSO4 + 2H2O
- Negative Plates:
- Material: The negative plates are typically made of sponge lead (Pb).
- Role: During discharge, the negative plates undergo a chemical reaction where sponge lead reacts with sulfuric acid to form lead sulfate and release electrons. This reaction complements the positive plate reaction, completing the overall electrochemical process.
- Charge Reaction: Pb + H2SO4 → PbSO4 + 2H+ + 2e-
- Charge and Recharge Process:
- During charging, the process is reversed. The positive plates convert lead sulfate back into lead dioxide, and the negative plates convert lead sulfate back into sponge lead. This allows the battery to store electrical energy for later use.
- The charge and discharge reactions involve the reversible conversion between lead dioxide (PbO2) and lead (Pb) at the positive and negative plates, respectively.
- Plate Structure:
- The plates are often constructed in a grid or mesh-like structure to increase the surface area, allowing for more active material and enhancing the battery’s capacity.
- The structure also helps support the active material and prevent shedding or deterioration during the cycling process.
- Separator:
- Between the positive and negative plates, there is usually a separator, often made of a porous material. The separator helps prevent short circuits by keeping the positive and negative plates from physically touching each other while allowing the flow of ions.
In summary, the positive and negative plates in lead-acid batteries are central to the electrochemical reactions that enable the storage and release of electrical energy. Their specific materials and structures are designed to facilitate the reversible conversion between lead dioxide and lead during charging and discharging cycles. The overall performance of the battery, including its capacity, voltage, and cycle life, is influenced by the characteristics of these plates.