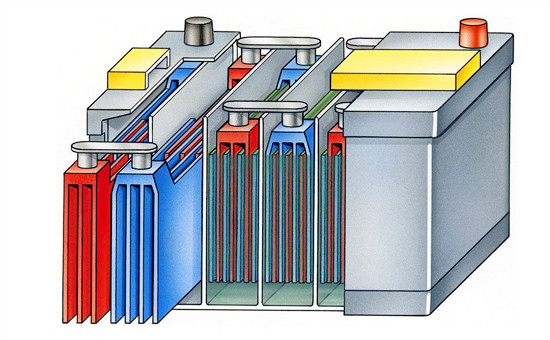
Lead-acid batteries typically consist of the following materials:
- Lead Dioxide (PbO2): This material serves as the positive electrode (cathode) in the battery.
- Spongy Lead (Pb): This material serves as the negative electrode (anode) in the battery.
- Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4): Sulfuric acid serves as the electrolyte in the battery. It facilitates the chemical reactions between the lead dioxide and spongy lead during charging and discharging.
- Lead Plates or Grids: These plates or grids provide structural support for the lead dioxide and spongy lead, and they also act as current collectors.
- Plastic Casing: Lead-acid batteries are typically encased in plastic to provide insulation and protect the internal components.
These materials undergo chemical reactions during the charging and discharging cycles of the battery, converting between lead dioxide, spongy lead, and lead sulfate.