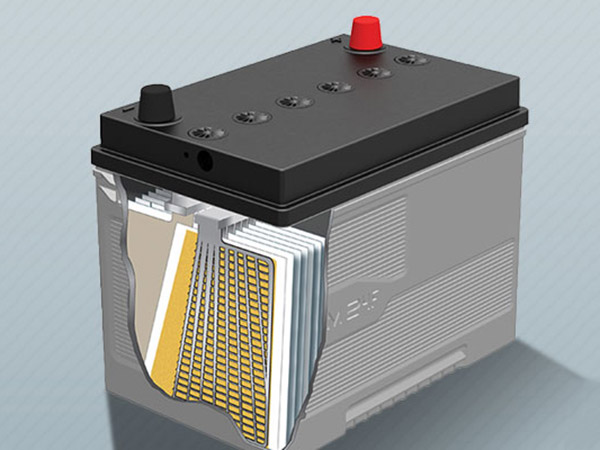
The environmental requirements for lead-acid battery discharge involve considerations for both the discharge process itself and the management of discharged batteries.
- Proper Disposal or Recycling: Lead-acid batteries contain hazardous materials such as lead and sulfuric acid. Discharging lead-acid batteries should be followed by proper disposal or recycling procedures to prevent environmental contamination. Recycling facilities can recover valuable materials like lead, plastic, and sulfuric acid for reuse, reducing the need for new resource extraction and minimizing environmental impact.
- Avoiding Contamination: During discharge, it’s essential to prevent leaks or spills of sulfuric acid, which is corrosive and harmful to the environment. Containment measures such as using appropriate containers and handling equipment can minimize the risk of spills.
- Ventilation: Lead-acid batteries release hydrogen gas during discharge, which can be explosive in certain concentrations. Adequate ventilation is necessary to disperse hydrogen gas safely. Discharging batteries in well-ventilated areas, or using battery enclosures with ventilation systems, helps mitigate the risk of hydrogen buildup.
- Monitoring Electrolyte Levels: Continuous discharge can lead to a decrease in electrolyte levels in lead-acid batteries. Monitoring electrolyte levels during discharge is crucial to prevent damage to the battery and ensure optimal performance. Maintaining proper electrolyte levels also reduces the risk of exposing lead plates, which can accelerate sulfation and decrease battery lifespan.
- Temperature Control: Lead-acid batteries perform best within a specific temperature range. Discharging batteries within this range helps maintain optimal performance and prolong battery life. Extreme temperatures can affect battery chemistry and lead to premature failure.
- Compliance with Regulations: Discharging lead-acid batteries must comply with relevant environmental regulations and guidelines. These regulations often dictate proper handling, disposal, and recycling practices to minimize environmental impact and ensure public safety.
- Safe Handling Practices: Proper training and safety protocols are essential for personnel involved in the discharge of lead-acid batteries. This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and safety glasses, as well as following established procedures to prevent accidents and injuries.
By adhering to these environmental requirements, the discharge of lead-acid batteries can be conducted safely and responsibly, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing resource efficiency.