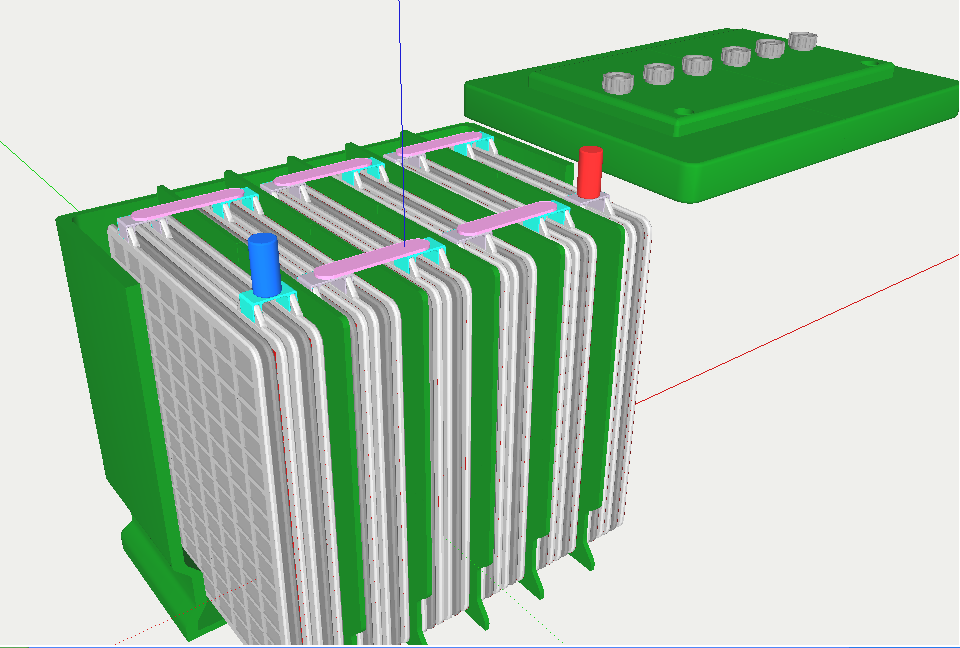
The production process of lead-acid batteries involves several stages, from raw material preparation to final assembly.
- Grid Production:
- Lead Alloy Preparation: The process begins with the preparation of the lead alloy, which is the primary material for the battery grids. Lead, along with small amounts of other elements like antimony or calcium, is melted to form the alloy.
- Grid Casting: The lead alloy is then cast into grids, which will serve as the support structure for the active material (lead dioxide and sponge lead) in the battery plates.
- Plate Production:
- Paste Formation: Lead oxide powder is mixed with sulfuric acid and other additives to create a paste. This paste is then applied to the grids, forming the positive and negative battery plates.
- Plate Curing: The newly formed plates are cured to allow the paste to harden and adhere properly to the grid.
- Assembly:
- Assembly of Battery Cells: The positive and negative plates are assembled with separators (often made of porous materials) in between to prevent short circuits. This assembly forms a complete cell.
- Formation: The cells undergo a formation process where they are filled with an electrolyte solution (usually sulfuric acid and water) and subjected to controlled charging and discharging cycles. This process activates the plates and establishes the initial capacity of the battery.
- Battery Case and Cover Production:
- Case Molding: Plastic cases for the batteries are molded to house the cells.
- Cover Production: Covers are produced to seal the battery and allow for venting.
- Assembly of Battery:
- Cell Insertion: The battery cells are inserted into the molded case.
- Connection: Inter-cell connections and terminal connections are made to complete the electrical circuit.
- Filling and Sealing:
- Electrolyte Filling: The batteries are filled with the final electrolyte solution.
- Sealing: The batteries are sealed to prevent leakage and to contain the electrolyte.
- Charge and Test:
- Charge: The batteries undergo a final charging process.
- Testing: Batteries are tested for capacity, voltage, and other performance parameters to ensure quality control.
- Final Inspection and Packaging:
- Inspection: The finished batteries undergo a final inspection for quality assurance.
- Packaging: Batteries are packaged and prepared for distribution.
It’s important to note that safety measures are implemented throughout the production process, especially during handling of lead and chemicals. Additionally, environmental considerations and recycling practices are integral to the lead-acid battery industry due to the materials involved.