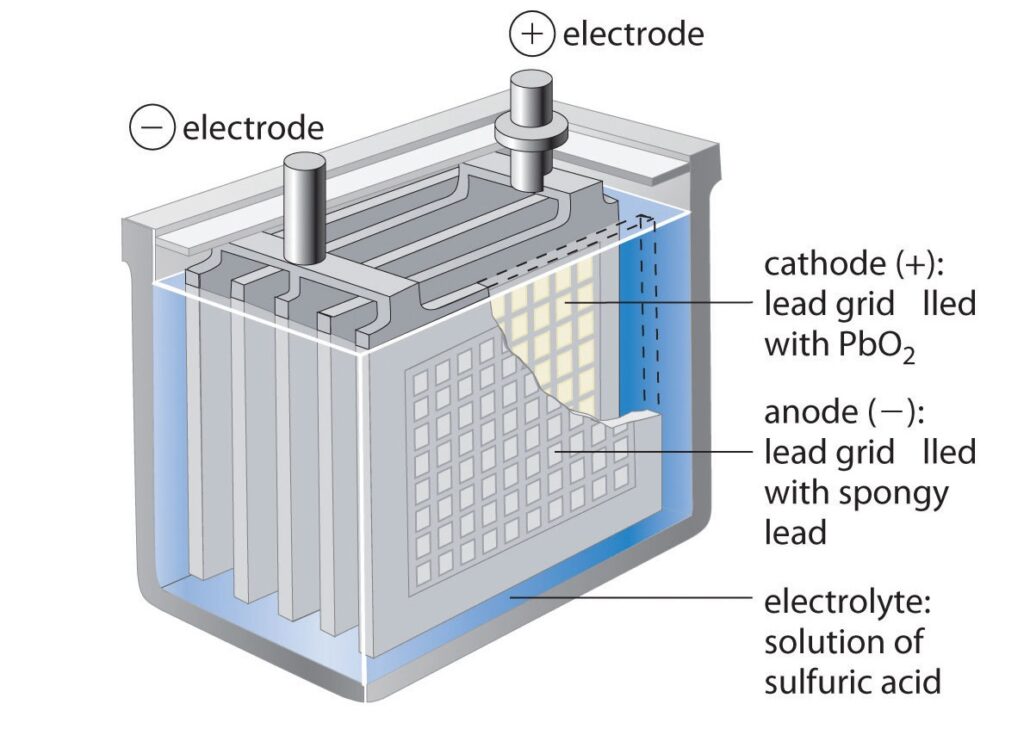
A lead-acid battery consists of several key components, each with its own function.
- Positive Plate (Cathode): The positive plate, also known as the cathode, is typically made of lead dioxide (PbO2) pasted onto a lead grid. Its main function is to react with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) during discharge, forming lead sulfate (PbSO4) and releasing electrons.
- Negative Plate (Anode): The negative plate, also known as the anode, is usually made of pure lead (Pb) or a lead alloy. Its primary function is to react with sulfuric acid during discharge, forming lead sulfate and releasing electrons.
- Separator: The separator is a porous material placed between the positive and negative plates to prevent them from coming into direct contact and causing a short circuit. The separator allows the flow of ions between the plates while preventing physical contact.
- Electrolyte: The electrolyte is a solution of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and water. Its main function is to facilitate the flow of ions between the positive and negative plates during charging and discharging. It also reacts with the plate materials to form lead sulfate during discharge.
- Battery Case: The battery case is typically made of plastic or other non-conductive materials and serves as a container to hold the electrolyte and plate assemblies. It provides structural support and protects the internal components from damage.
- Terminal Posts: The terminal posts are metal posts located on the top of the battery case. They serve as connection points for external electrical circuits, allowing the battery to be connected to devices or other batteries in series or parallel configurations.
- Vent Caps: Vent caps are typically located on top of the battery case and serve as openings for the release of gases generated during charging. They help regulate internal pressure and prevent the buildup of hydrogen gas, which can be hazardous.
- Plate Grids: The plate grids provide structural support for the active material (lead dioxide on the positive plate and lead on the negative plate). They also serve as conductors, allowing the flow of electrons during charging and discharging.
Each of these components plays a crucial role in the operation of a lead-acid battery, facilitating the electrochemical reactions that store and release electrical energy.