Lead-acid batteries can be classified into different types based on their design, construction, and specific applications.
- Flooded Lead-Acid Batteries:
- Also known as vented or wet-cell batteries, flooded lead-acid batteries have a liquid electrolyte (dilute sulfuric acid) that is free to move within the cell. The cells have vent caps to allow the release of gases produced during charging. These batteries require periodic maintenance to check and replenish the electrolyte level and are commonly used in automotive applications.
- Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA) Batteries:
- VRLA batteries are sealed batteries that use a valve mechanism to regulate gas pressure within the battery. This category includes two subtypes:
- AGM batteries use a fiberglass mat as a separator to absorb and immobilize the electrolyte. They are maintenance-free, have a relatively low self-discharge rate, and are commonly used in applications like uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, renewable energy storage, and recreational vehicles.
- Gel batteries use a silica gel to immobilize the electrolyte. This gel creates a semi-solid state, reducing the risk of acid leakage. Gel batteries are often used in deep-cycle applications, such as solar power systems and electric wheelchairs.
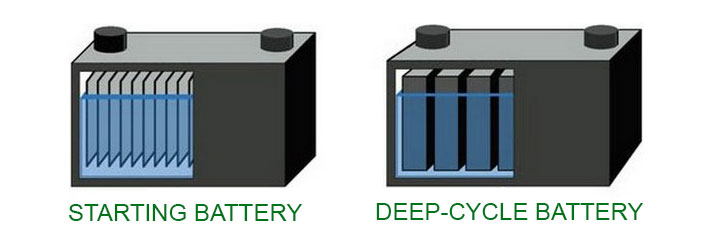
- Deep-Cycle Batteries:
- Deep-cycle batteries are designed to withstand repetitive deep discharges and recharges. They are commonly used in applications where sustained power over a longer period is required, such as in electric golf carts, forklifts, renewable energy systems, and marine applications.
- Starting, Lighting, and Ignition (SLI) Batteries:
- SLI batteries, also known as automotive batteries, are designed to provide a high burst of energy for a short duration, making them suitable for starting the engine, powering lights, and running other electrical accessories in vehicles.
- Stationary Batteries:
- Stationary batteries are designed for applications where the battery remains in a fixed location, such as backup power systems, UPS systems, and telecommunication infrastructure. These batteries are often deep-cycle or VRLA batteries.
- Dual-Purpose Batteries:
- Dual-purpose batteries are designed to serve both starting and deep-cycle functions. They are commonly used in marine applications where a single battery is required to start the engine and power onboard electronics.
The choice of lead-acid battery type depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the need for maintenance, cycle life, discharge characteristics, and environmental considerations. Each type has its advantages and limitations, making them suitable for different use cases.