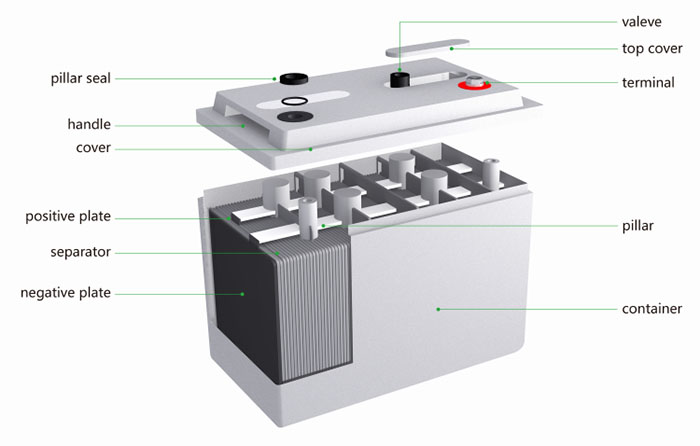
Lead-acid batteries consist of several key components, and their structure is designed to facilitate the electrochemical reactions that occur during the charging and discharging processes. The basic components of a lead-acid battery include:
- Positive Plate (Cathode):
- The positive plate is typically made of lead dioxide (PbO2). Lead dioxide serves as the active material for the positive electrode, and it undergoes chemical reactions during both discharge and charge cycles.
- Negative Plate (Anode):
- The negative plate is composed of sponge lead (Pb). Sponge lead acts as the active material for the negative electrode and also undergoes chemical reactions during the battery’s operation.
- Separator:
- The separator is a porous material placed between the positive and negative plates to prevent direct electrical contact between them. It allows the flow of ions while preventing short circuits.
- Electrolyte:
- The electrolyte in a lead-acid battery is a solution of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and water. The electrolyte facilitates the movement of ions between the positive and negative plates during the electrochemical reactions.
- Cell Container:
- The cell container is typically made of plastic and serves as the outer casing that holds all the components together. It also houses the electrolyte.
- Vent Caps:
- Vent caps are typically present on each cell of the battery and serve as a way for gases produced during charging to escape while preventing the entry of external contaminants.
- Terminal Posts:
- Terminal posts are the connection points where external electrical connections are made to the battery. These posts allow the flow of electrical current into and out of the battery.
The overall structure of a lead-acid battery involves multiple cells connected in series to achieve the desired voltage. Each cell consists of one positive plate, one negative plate, and a separator, immersed in an electrolyte solution. The cells are connected in series to increase the voltage, and the entire assembly is housed in a container.
During discharge, the chemical reactions at the electrodes lead to the conversion of lead dioxide at the positive plate to lead sulfate, and sponge lead at the negative plate is also converted to lead sulfate. During charging, these reactions are reversed, converting lead sulfate back into lead dioxide at the positive plate and sponge lead at the negative plate.
It’s important to note that lead-acid batteries are often categorized into different types, such as flooded lead-acid batteries, where the electrolyte is in liquid form, and valve-regulated lead-acid (VRLA) batteries, which include absorbent glass mat (AGM) and gel batteries, where the electrolyte is immobilized in some way, either by being absorbed in a mat or immobilized in a gel. Each type has its specific advantages and applications.