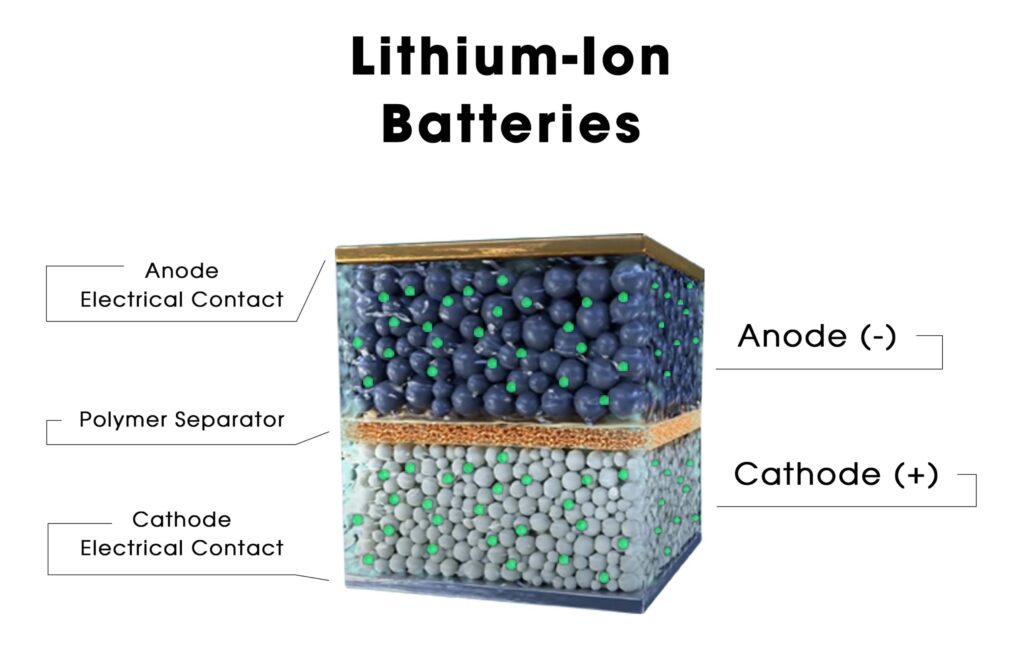
Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4 or LFP) is a type of rechargeable lithium-ion battery that is known for its high energy density, long cycle life, and safety features. The composition and structure of a lithium iron phosphate battery include the following key components.
- Cathode (Positive Electrode):
- The cathode is typically composed of lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) as the active material. LiFePO4 is a compound made up of lithium ions (Li+), iron (Fe), and phosphate (PO4).
- The crystal structure of LiFePO4 is olivine-like, and it provides stability during charging and discharging cycles.
- Anode (Negative Electrode):
- The anode is usually made of a form of carbon, such as graphite. During discharge, lithium ions move from the anode to the cathode, and during charging, they move from the cathode back to the anode.
- Electrolyte:
- The electrolyte is a conductive solution that facilitates the movement of lithium ions between the cathode and anode during the electrochemical reactions.
- Commonly, a lithium salt dissolved in a solvent, such as lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6) in a mixture of ethylene carbonate (EC) and dimethyl carbonate (DMC), is used as the electrolyte in lithium iron phosphate batteries.
- Separator:
- The separator is a permeable membrane that physically separates the cathode and anode to prevent short circuits while allowing the transport of lithium ions.
- Current Collectors:
- Both the cathode and anode have current collectors, typically made of aluminum for the cathode and copper for the anode. These collectors help in the flow of electric current to and from the external circuit.
- Enclosure and Packaging:
- The entire battery is enclosed in a casing or packaging to protect the internal components and ensure safety.
The overall reaction during the discharge process in a lithium iron phosphate battery can be represented as follows:
LiFePO4→DischargeLi++FePO4LiFePO4DischargeLi++FePO4
During charging, the reaction is reversed:
Li++FePO4→ChargeLiFePO4Li++FePO4ChargeLiFePO4
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are known for their thermal stability, reduced risk of thermal runaway, and improved safety compared to some other lithium-ion battery chemistries. They find applications in various devices, including electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems.